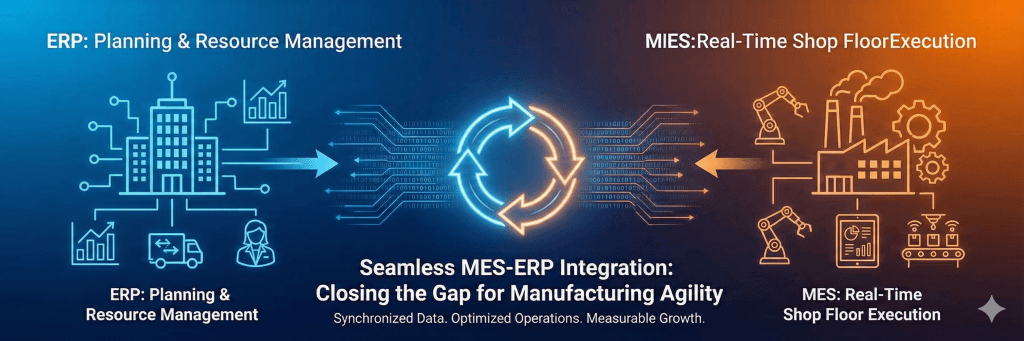
MES integration changes the way manufacturers handle their business operations and production processes. But many companies face challenges with disconnected systems that create inefficiencies and data gaps in their operations.
Companies that connect their MES with ERP systems get live data sync and a detailed view of their manufacturing lifecycle. This integration helps businesses streamline processes, combine data silos, and respond to changes with better agility. On top of that, it lets organizations cut down order fulfillment time, reduce warehouse inventory duration, and maintain product quality through tight data connections. The system creates a closed loop where ERP plans production, MES executes it, and the results flow back to improve continuously.
In this piece, we’ll show you how to achieve uninterrupted MES and ERP integration. You’ll learn about system compatibility and best practices that bring measurable ROI to your manufacturing operations.
Defining MES and ERP: What They Do and How They Differ
You should know the difference between Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) before starting any integration project. These systems work together but serve different purposes in the manufacturing ecosystem.
MES: Real-Time Shop Floor Monitoring and Control
A Manufacturing Execution System works like the central nervous system of your production floor. MES software tracks, monitors, and documents how raw materials transform into finished products in real time. The system connects to factory machinery through sensors, barcode scanners, and operator inputs to collect immediate data about production-floor operations.
We focused on day-to-day execution with MES. The system provides detailed control of production scheduling and manufacturing quality. It tracks work-in-progress, machine statuses, and production bottlenecks as they happen. This allows manufacturers to adjust their operations instantly. MES also makes sure every product meets specifications and quality standards.
MES shines in its ability to show the complete picture of factory floor performance. This visibility helps manufacturers:
- Monitor production in real time across the entire production cycle
- Analyze production performance and optimize operations
- Enforce quality control procedures and minimize waste
- Maximize equipment uptime and resource utilization
- Enable traceability and compliance, especially important for regulated industries
ERP: Enterprise-Wide Resource and Process Management
ERP systems take a broader approach compared to MES’s shop floor focus. Modern ERP solutions evolved from manufacturing resource planning (MRP II) systems. They now serve as the operational backbone for business operations. These systems blend various business processes into a unified system with a central database.
ERP systems offer a high-altitude view of business operations and coordinate functions across departments. They include:
- Finance and accounting management
- Human resources and payroll
- Inventory and supply chain management
- Procurement and vendor relationships
- Customer relationship management
- Sales and marketing
ERP determines what and when products will be made. It handles strategic planning aspects of production. The system helps with forecasting, budgeting, and resource allocation from an enterprise-wide viewpoint. Decision-makers can analyze each part of the business as a whole.
Overlap and Gaps Between MES and ERP Systems
MES and ERP systems share some functions, especially in inventory management and production tracking. This can create redundancies if you don’t design the integration well.
The main difference lies in how they operate:
- MES works at the execution level with a shop-floor focus and collects detailed, up-to-the-minute data analysis
- ERP works at a planning level with an enterprise-wide focus and provides strategic oversight
The gap between these systems often shows up as a mismatch between planned production (ERP) and actual execution (MES). Poor integration creates several challenges:
- Data inconsistencies between systems
- Manual data entry and potential human errors
- Delayed information flow between planning and execution
- Limited visibility across the production lifecycle
MES-ERP integration fixes these gaps. It helps coordinate production activities with inventory management, logistics, sales, and customer service. This coordination improves demand forecasting, inventory management, cash flow, and customer satisfaction.
Why MES ERP Integration is Critical for Growth
Manufacturers who want to grow their operations should think about how MES integration with ERP systems can improve their capabilities. This connection closes the gap between production realities and business planning and creates new ways to improve efficiency.
Breaking Down Data Silos Across Operations
Many legacy manufacturing companies work with isolated information trapped in different departments and systems. PWC research shows that modernizing data and eliminating data silos ranks as a top priority for manufacturing CIOs in 2024. Isolated data storage often results from legacy systems, departmental boundaries, and poor data management.
These separate data environments create major problems:
- Teams waste time gathering and reconciling data which delays decisions
- Departments produce redundant or inconsistent reports
- Resource utilization remains unclear
- Companies miss chances to optimize and face higher risks
MES ERP integration solves these problems by creating a central data hub. This unified system stores all critical information about customers, suppliers, production, inventory, and logistics. Companies can standardize their data formats, protocols, and naming conventions to keep all systems and processes consistent.
Arranging Production with Business Objectives
ERP and MES systems working together give manufacturers a chance to use their combined strengths. Aberdeen Group’s survey shows impressive results – 57% of manufacturers using integrated ERP and MES systems coordinate operations with customer service, logistics, and delivery (compared to 26% of others), and 53% standardize production planning and execution (versus 27% of others).
MES provides ERP with current production data including:
- Parts and serial number usage
- Current production levels
- Scrap material quantities
- Equipment performance metrics
This two-way data flow helps manufacturers sync production activities with business goals. ERP manages top-level demand from forecasts and customer orders, then applies it to tactical planning—where MES takes control. These systems create a feedback loop where planning guides execution and results improve future plans.
Supporting Agile Manufacturing and Demand Changes
Today’s unpredictable market makes knowing how to adapt to demand changes a significant competitive edge. Integration enables synchronized planning and scheduling in manufacturing and business processes. Production volumes can adjust quickly to changing demand patterns.
MES-ERP integration improves resource allocation by showing equipment use, worker availability, and material needs across manufacturing. Integrated systems let manufacturers:
- Order supplies before inventory gets too low to avoid rush orders
- Cut warehouse costs with just-in-time inventory
- Adapt production schedules to customer demands quickly
- Group jobs strategically to use resources better
This flexibility extends beyond internal operations. Integration makes order fulfillment smooth by keeping order information, production schedules, and inventory levels in sync. Manufacturers can respond quick to market changes while maintaining quality and efficiency.
This powerful combination of ERP’s planning capabilities and MES’s tactical advantages gives manufacturers flexibility and responsiveness throughout their operations.
Planning a Seamless MES Integration with ERP
A careful planning process forms the foundations of successful MES integration with erp. The right approach will maximize system value and deliver operational excellence. Your digital manufacturing environment needs a continuous thread that reduces disruptions and keeps stakeholders in sync.
Conducting a System Compatibility Assessment
The first step requires a review of your current manufacturing processes, systems, and pain points. This helps understand technical limitations and integration possibilities. Your assessment should look at:
- Existing connections between shop floor equipment and enterprise systems
- Data structures and formats in both environments
- Legacy constraints that might affect integration
- Supported technologies and protocols across systems
Manufacturing teams must identify which lines, machines, metrology equipment, and key applications like ERP or CMMS need data exchange. A full picture confirms data integrity and prepares employees for new workflows. The choice between on-premise or cloud hosting depends on your operational criticality and scheduling needs.
Setting Clear Integration Goals and KPIs
Your integration objectives need definition before implementation starts. The team should document data sharing requirements, frequency, and the specific cells or tables for communication. These objectives link to measurable KPIs such as:
- Reduced production costs
- Accelerated lead times
- Improved inventory accuracy
- Better production visibility
These metrics guide implementation decisions and help measure success. A cross-functional implementation team with IT, operations, production, quality, and management stakeholders ensures project alignment.
Selecting the Right Integration Architecture
Your existing infrastructure determines the best integration approach. The common architectural options include:
- Middleware Solutions – These act as intermediaries between systems and handle communication protocols, data transformations, and errors.
- API-Based Integration – Direct system communication through application programming interfaces gives complete data control but needs more development work.
- ISA-95 Standards – B2MML (Business-to-Manufacturing Markup Language) and OPC UA ensure consistent communication across vendors.
- Functional Namespace – Industry 4.0 approaches use custom connections that let users create custom KPIs for immediate process optimization.
Your chosen architecture should validate data and support both batch and real-time sync methods based on business needs. Manufacturers with multiple plants need solutions that standardize master data while allowing plant variations.
A reliable integration architecture builds your connected manufacturing ecosystem. This bridges operational technologies with business systems and provides unprecedented visibility and control.
Best Practices for Successful ERP and MES Integration
MES integration with ERP needs more than just technical connection—it needs careful planning and systematic implementation. These best practices will give a smooth integration project that delivers maximum value with minimal disruption.
Standardizing Data Formats and Naming Conventions
Standardization creates the foundation for successful ERP and MES integration. Common data formats like XML, JSON, or EDI create a universal language between systems. RESTful APIs or web services make the connection process simpler. Beyond formats, semantic consistency plays a vital role—similar naming conventions and IDs across systems prevent confusion.
Data validation tools must work alongside standardization efforts. These tools check accuracy, completeness, and consistency during exchanges to build a reliable information foundation.
Getting Cross-Functional Teams Involved Early
The system’s success depends on production, quality, finance, supply chain, and IT departments working together from day one. This team approach helps meet operational needs throughout the organization and builds significant support from stakeholders.
Cross-functional teams help bridge gaps between office staff and shop floor personnel, which reduces resistance to change. Daily stand-ups, sprint planning meetings, and retrospective sessions encourage alignment among teams of all types.
Implementing Gradual Rollouts and Pilot Testing
The best approach starts with a pilot program on one production line or process. Organizations can confirm each integration step while maintaining product quality. System testing before scaling up reduces risk and disruption.
Testing should happen in different scenarios and conditions to check accuracy and reliability. A sandbox environment gives employees a safe space to practice tasks like data entry and workflow processing.
Training Staff on New Workflows and Tools
Employee training determines MES-ERP integration success. Role-based training modules let each department focus on relevant ERP and MES tools. Custom workshops that focus on department-specific functions create an effective learning experience.
A mix of in-person training, online modules, and self-paced learning works well with different learning priorities. Regular refresher courses help reinforce knowledge and introduce system updates.
Ensuring Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance
Integration needs constant attention after implementation. Monitoring systems track data flows, system performance, and user interactions. Quick action resolves issues and keeps business operations running smoothly.
Good documentation of integration architecture, configurations, and processes helps future reference. Change management practices handle updates or modifications to either system, while impact assessments minimize disruptions. Regular system audits help find areas to improve performance.
Measuring ROI and Long-Term Value of Integration
Measuring MES integration benefits starts with setting clear metrics linked to business goals. Many manufacturers find it hard to measure returns, but good measurement helps secure ongoing support and optimize performance.
Operational Efficiency Gains and Cost Savings
MES integration with ERP brings significant financial benefits in several ways. Companies using these integrated systems cut operating costs by optimizing stock levels. This ensures they avoid both excess inventory that raises storage costs and insufficient supply that leads to lost revenue. Automated inventory management can trigger orders or alert purchasing managers when needed, which creates just-in-time efficiency.
The integration of MES and ERP cuts down manual data entry and reduces errors that affect entire organizations. Staff members can focus on strategic, value-adding work instead of tedious data checking.
Improved Customer Satisfaction Through Faster Fulfillment
Better customer service stands out as a vital ROI measurement area. The system lets manufacturers track key metrics like on-time delivery rates, order accuracy, support team response times, and Net Promoter Score. Companies can also speed up order fulfillment and reduce warehouse storage time.
Manufacturers can give customers real-time updates on production status through smooth integration, which builds trust and transparency. In fact, this visibility covers the whole order process, from placement through manufacturing and delivery.
Scalability and Future-Proofing Manufacturing Systems
The system’s long-term value comes from its ability to adapt to changing business needs. Integrated systems handle growing transaction volumes, periodic surges, and business development. Cloud-based solutions cost less to set up and maintain than on-premises systems, which brings immediate benefits while spreading costs over time.
The system makes production more flexible by adjusting order processing and matching schedules with current needs. MES ERP integration helps manufacturers adopt emerging technologies like AI, machine learning, and advanced robotics while improving collaboration across the entire value chain.
Conclusion
Manufacturing excellence needs uninterrupted connection between planning systems and shop floor execution. We have explored how MES integration with ERP creates a digital thread. This integration turns manufacturing operations from siloed functions into a cohesive ecosystem. The system bridges the gap between high-level business planning and immediate production activities.
Companies gain competitive advantages when they implement this integration successfully. Immediate data synchronization leads to faster decisions. Standardized information flows remove redundant data entry and human errors. On top of that, manufacturers become more agile. They respond quickly to market changes and customer needs without compromising quality or efficiency.
The integration trip needs careful planning and systematic implementation. Start with a thorough compatibility assessment of your current systems. Set clear goals with measurable KPIs before choosing the right integration architecture. Data formats must be standardized. The core team should be involved early to ensure support across departments.
Step-by-step rollouts and complete testing reduce disruption and confirm integration benefits. Team training on optimized workflows becomes crucial for adoption. Continuous monitoring helps maintain peak performance over time.
The value goes beyond operational improvements. Integrated MES-ERP systems cut costs through inventory optimization, fewer manual processes, and optimized production. Customers become happier due to faster fulfillment and better transparency. Maybe even more crucial, this integration builds a foundation for future growth. Manufacturers can scale operations and adopt new technologies easily.
Manufacturers who accept new ideas about MES-ERP integration set themselves up for lasting success in an ever-changing competitive world. The unified view of operations from order to delivery creates unprecedented visibility and control. Manufacturing data becomes a strategic asset that drives continuous improvement and breakthroughs.
Key Takeaways
Successful MES-ERP integration transforms manufacturing operations by connecting real-time shop floor data with enterprise-wide planning, creating a unified digital ecosystem that drives operational excellence and competitive advantage.
• Break down data silos: Integrate MES and ERP to eliminate isolated information pockets, enabling real-time visibility across production and business operations for faster decision-making.
• Start with thorough planning: Conduct system compatibility assessments, set clear KPIs, and involve cross-functional teams early to ensure seamless integration and stakeholder buy-in.
• Implement gradually with standardization: Use pilot testing, standardize data formats, and provide comprehensive staff training to minimize disruption while maximizing adoption success.
• Measure tangible ROI: Track operational efficiency gains, reduced inventory costs, faster order fulfillment, and improved customer satisfaction to demonstrate integration value.
• Build for future scalability: Choose integration architectures that accommodate growth, emerging technologies, and changing business needs while maintaining operational flexibility.
When executed properly, MES-ERP integration creates a closed-loop system where planning informs execution and execution results refine future planning, delivering measurable improvements in cost reduction, customer satisfaction, and manufacturing agility.
FAQs
Q1. What are the main benefits of integrating MES with ERP systems? Integration of MES with ERP systems breaks down data silos, aligns production with business objectives, and supports agile manufacturing. It enables real-time data synchronization, streamlines processes, and provides a comprehensive view of the entire manufacturing lifecycle.
Q2. How can manufacturers ensure a successful MES-ERP integration? To ensure successful integration, manufacturers should conduct a thorough system compatibility assessment, set clear integration goals and KPIs, select the right integration architecture, standardize data formats, involve cross-functional teams early, and implement gradual rollouts with pilot testing.
Q3. What are some key considerations when selecting an integration architecture for MES and ERP? When selecting an integration architecture, consider options like middleware solutions, API-based integration, ISA-95 standards, and functional namespace approaches. The chosen architecture should enable data validation mechanisms and support both batch and real-time synchronization based on specific business needs.
Q4. How does MES-ERP integration improve customer satisfaction? MES-ERP integration improves customer satisfaction by enabling faster order fulfillment, reducing warehouse inventory duration, and providing real-time updates on production status. This increased transparency and efficiency throughout the order fulfillment process builds trust with customers.
Q5. What long-term value does MES-ERP integration offer manufacturers? MES-ERP integration offers long-term value through enhanced scalability and future-proofing of manufacturing systems. It allows manufacturers to accommodate growing transaction volumes, adapt to changing business needs, and embrace emerging technologies like AI and machine learning, positioning them for sustained success in a competitive landscape.